Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Examples

Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
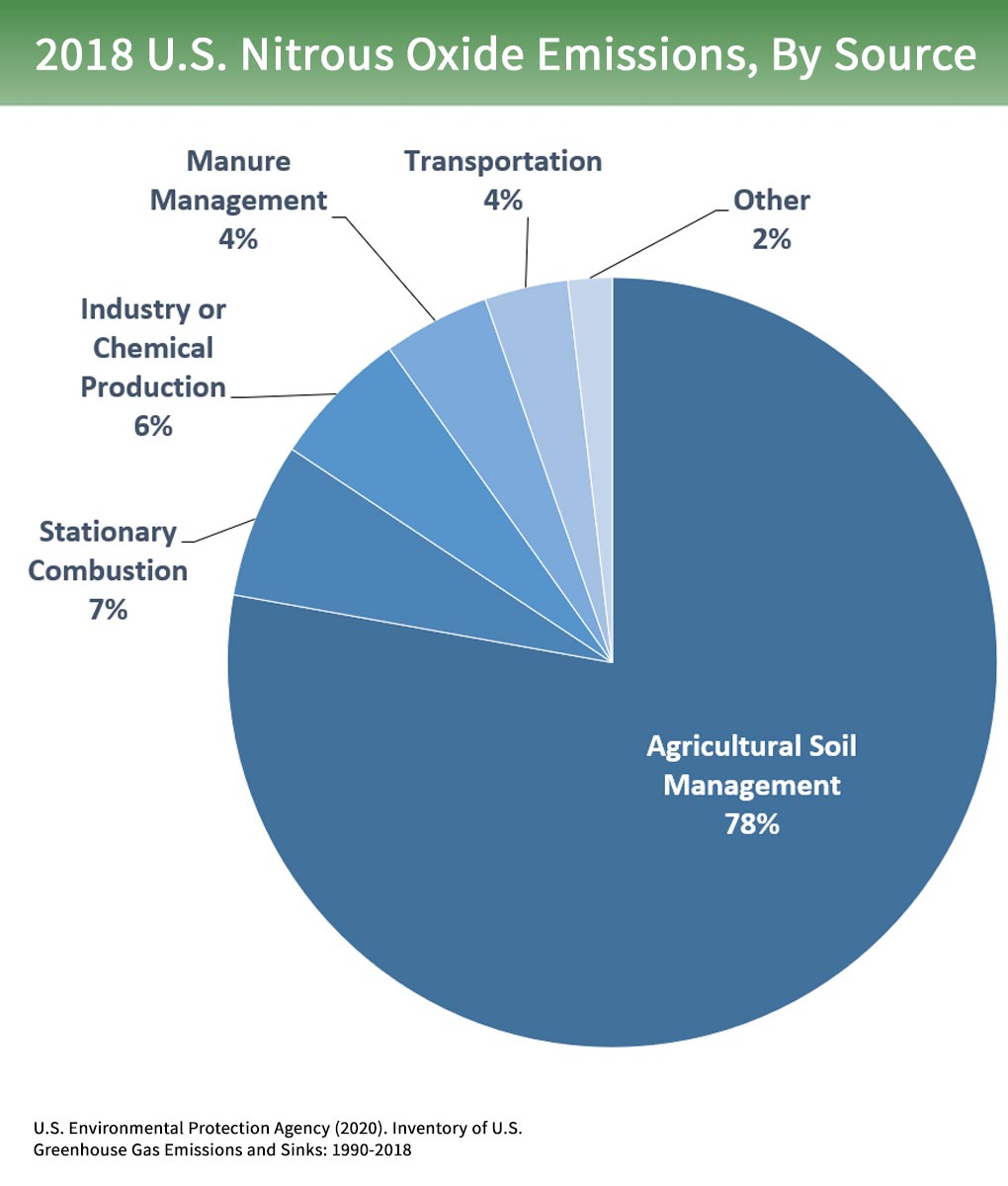
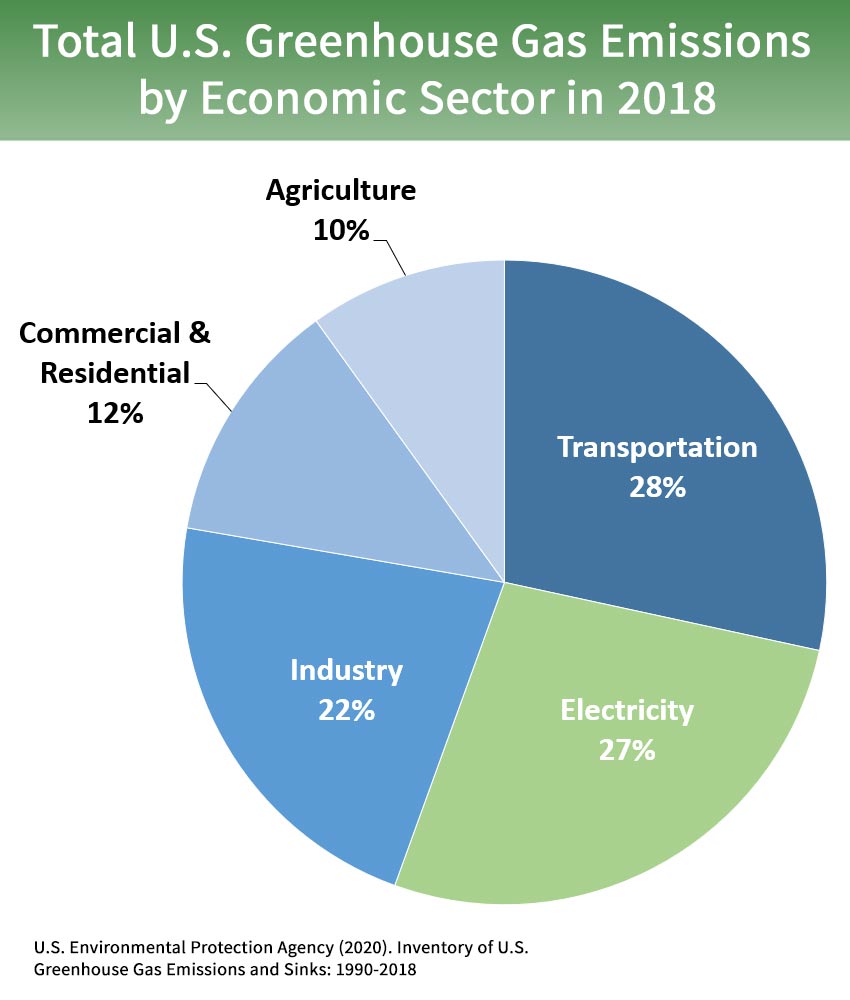
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Rach Rob Pop Up Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Models Following A Geography Lesson On The Causes Of Climatechange For Year 8 A Task That Encourages Creativity And Aids Understanding Of
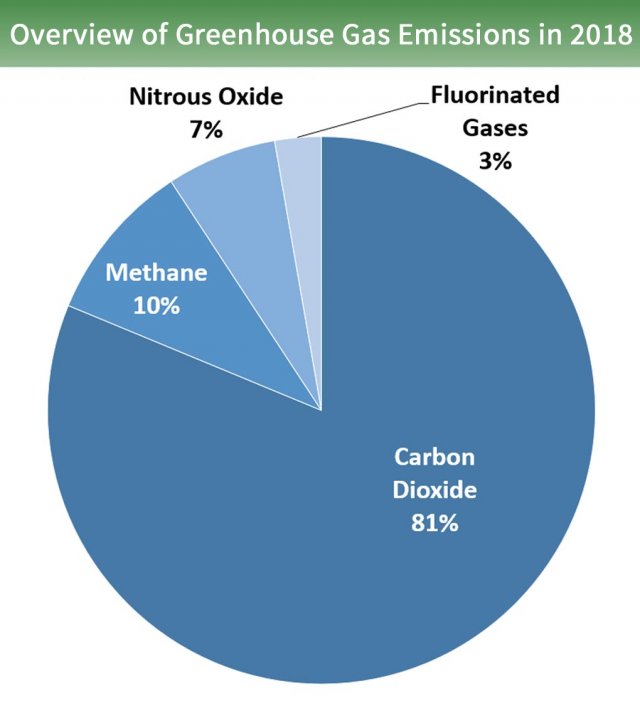
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
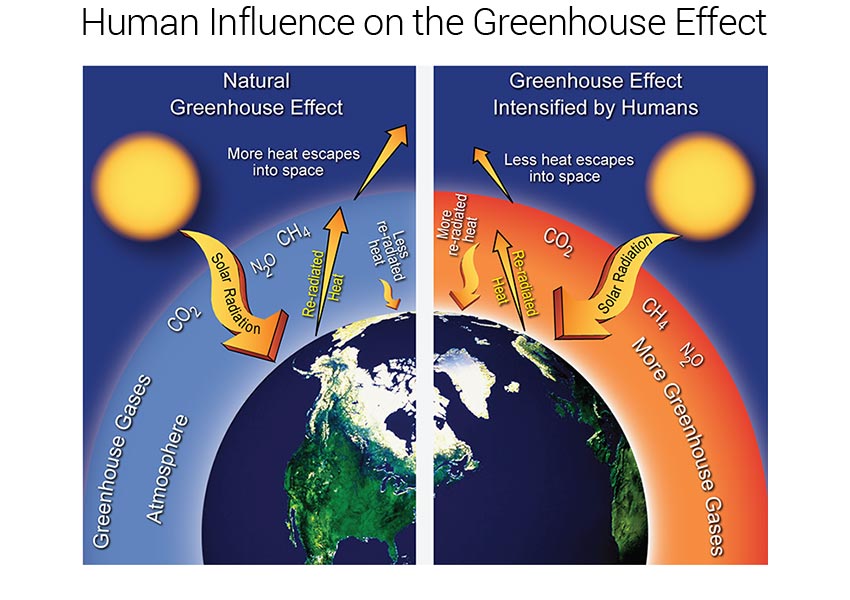
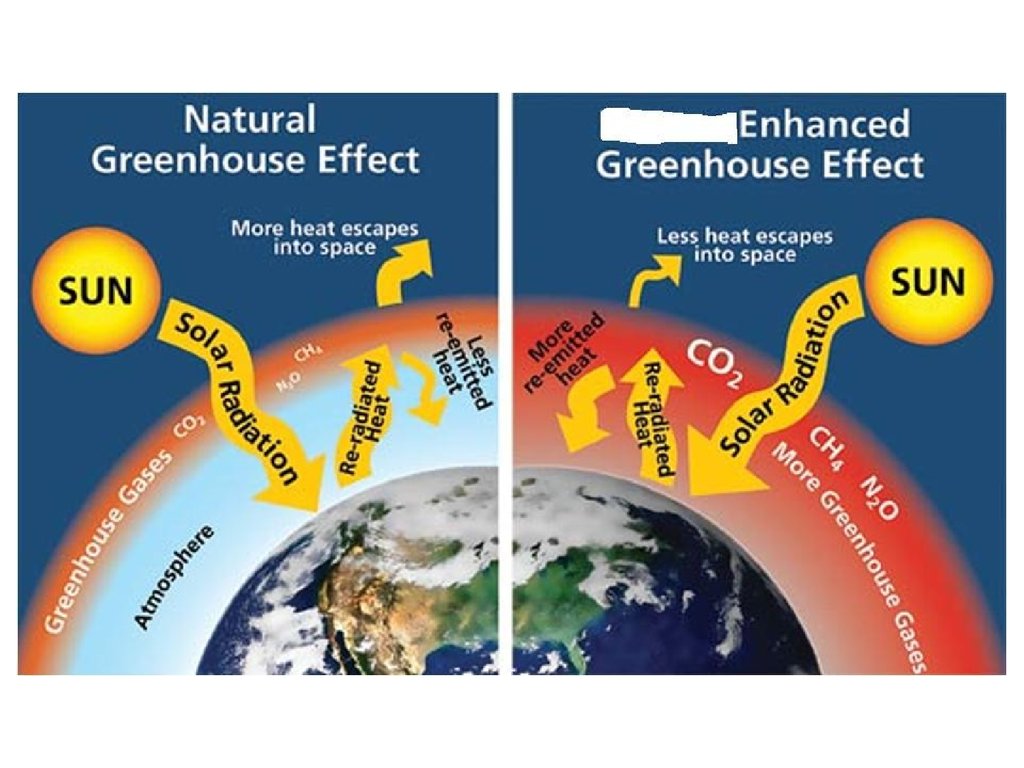
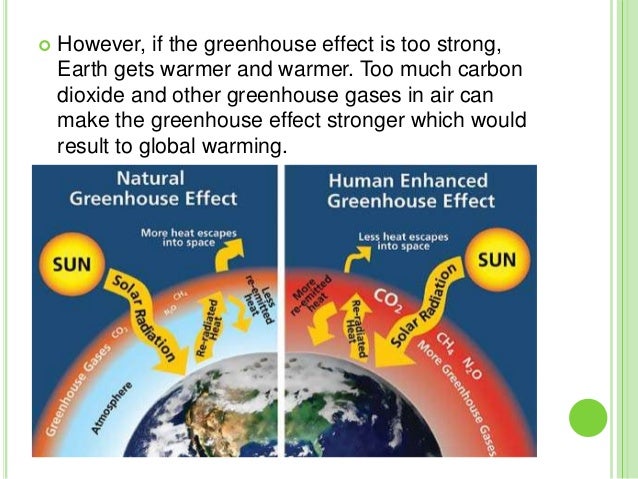
Adding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth’s surface and lower atmosphere even warmer.

Enhanced greenhouse effect examples. The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be. The magnitude of the enhanced greenhouse effect is influenced by various complex interactions in the earth-ocean-atmosphere system which are not included in the discussion above. Farming cattle releases methane.
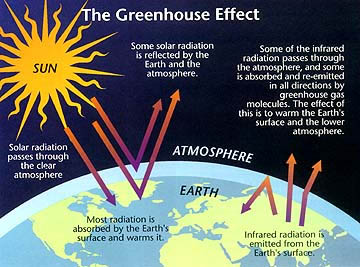
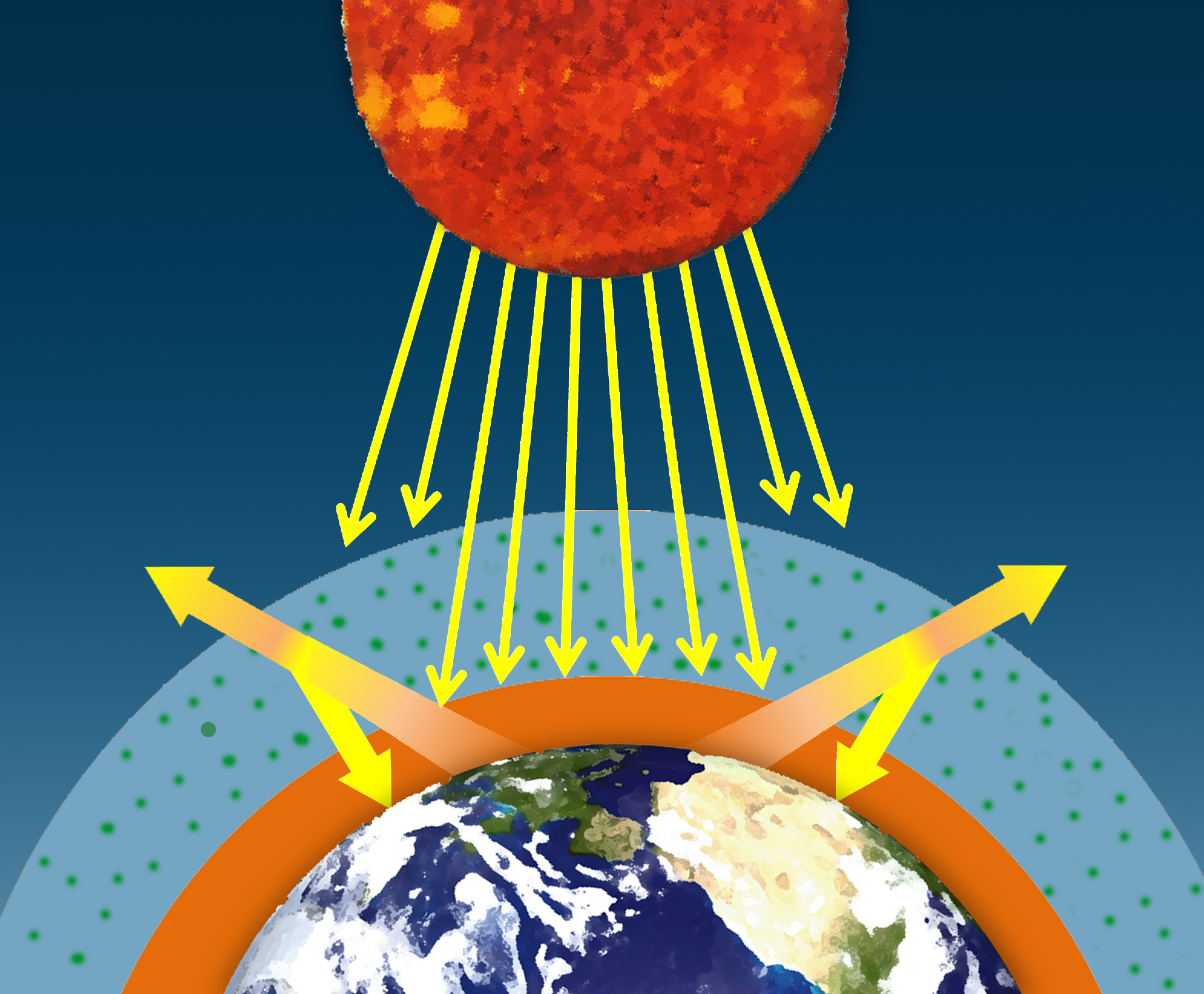
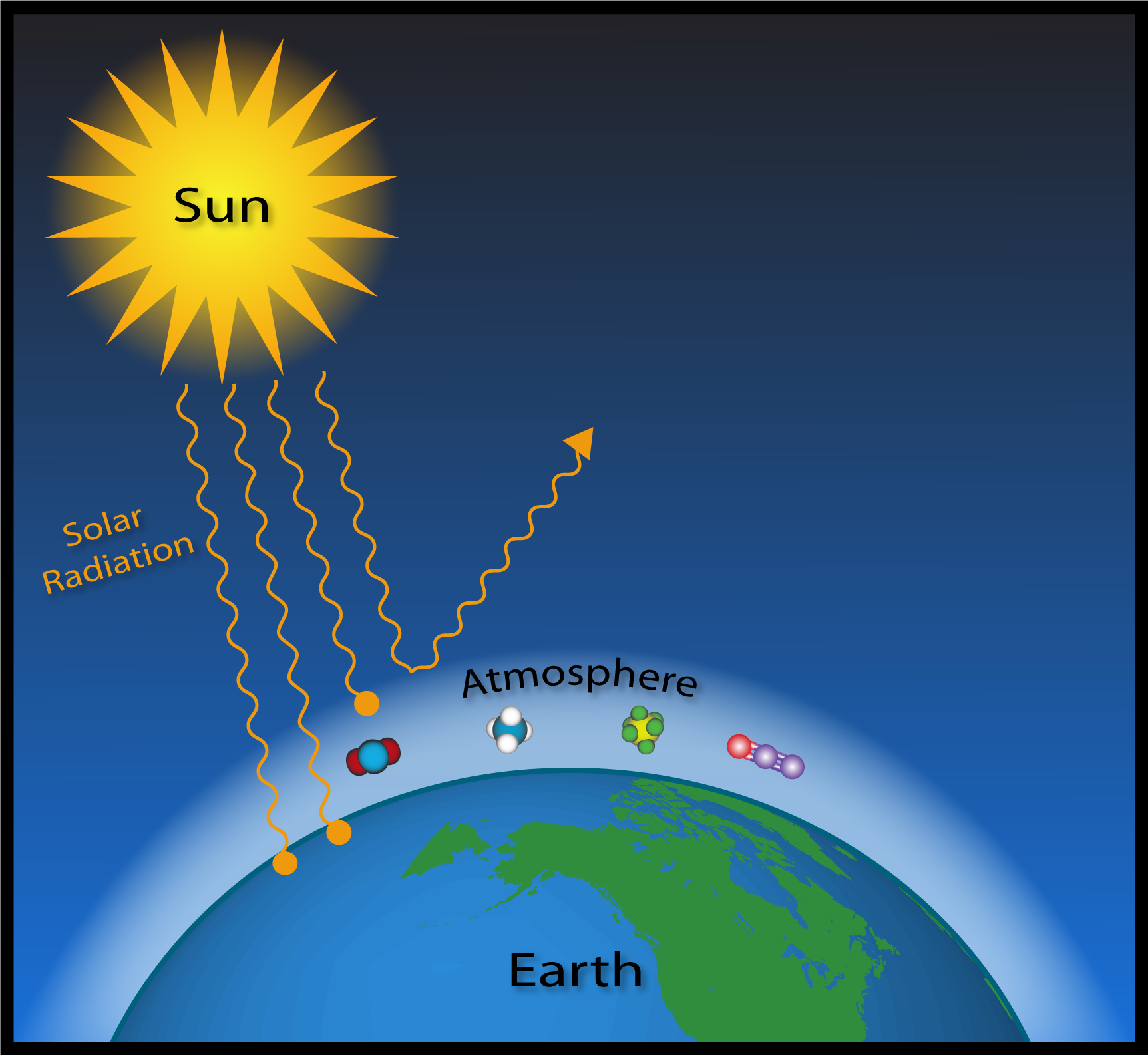
This in turn raises the temperature and causes even more ice to melt. The sun emits shortwave radiation, which passes through Earth's atmosphere and is absorbed by Earth's surface. Greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which thermal radiation from earth’s surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions.
Some of the major green house gases are. A short video explaining the enhanced greenhouse effect. Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to human activities that are adding to the warming of the atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect —the presence of gases that increases the atmosphere's retention of the heat energy of the sun. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effect. The trapping of the long wavelength radiation leads to more heating and a higher resultant temperature.
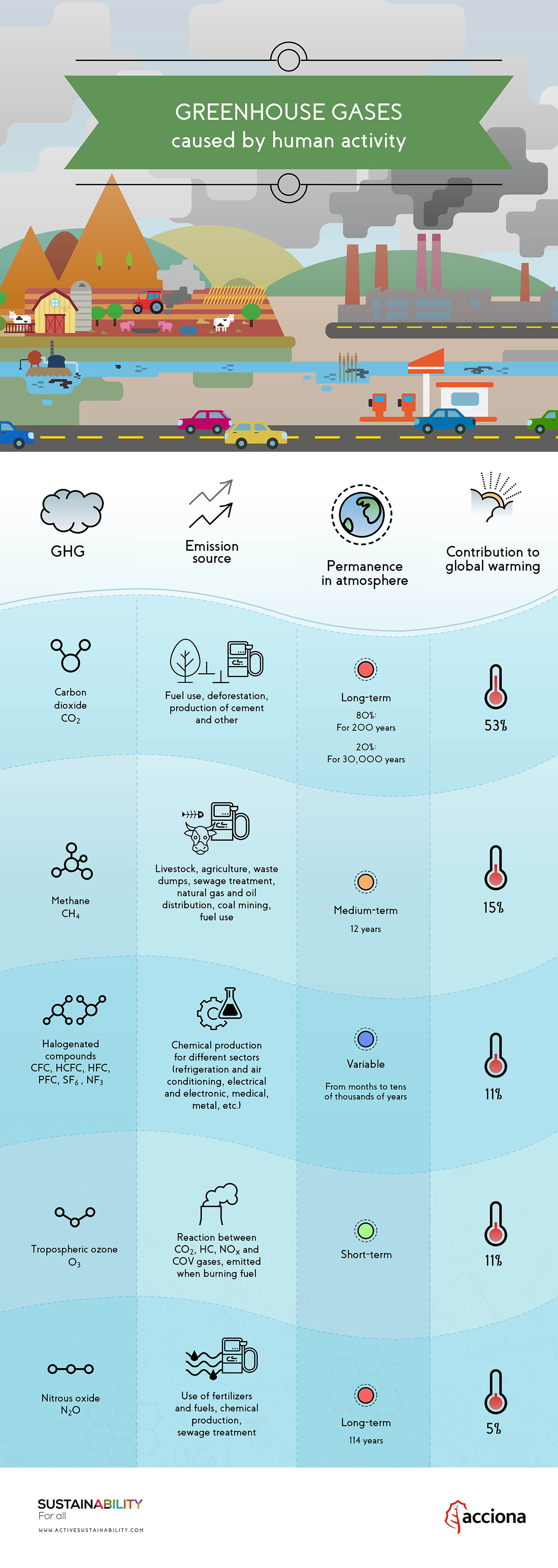
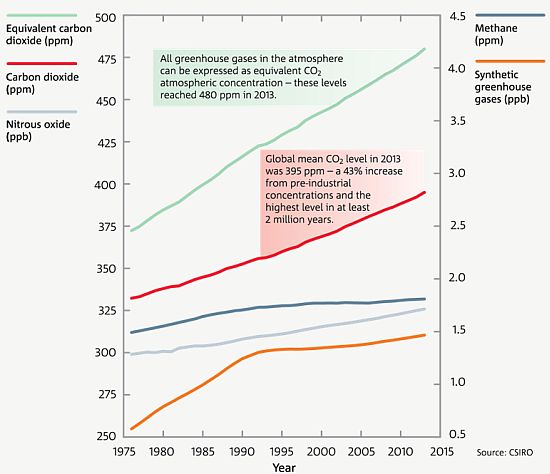
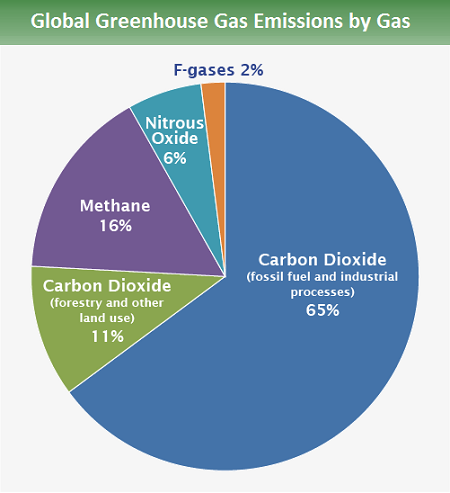
Water vapor is a greenhouse gas, as well as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and several other gases. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides. Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide are major gases responsible for this enhanced greenhouse effect (Table 1).
The problem is that our increased release of greenhouse gases is causing an increase in the greenhouse effect called the enhanced greenhouse effect. Such as carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, etc.) absorb the infra red radiation (heat) which is converted into kinetic and potential energy. Because CFC-12 is a large, heavy molecule with many atoms and a.
( larger version) Greenhouse gases affect Earth’s energy balance and climate. Sunlight passes through the atmosphere. Additionally, it is used as a refrigerant.
Increasing atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere are causing global air and ocean temperatures to rise As air temperature increases, glaciers and ice sheets shrink—they lose more ice from melting and calving (iceberg formation) than they gain from snowfall—and this adds more water to the ocean. The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to a rise of the equilibrium temperature at the earth’s surface due to anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. For example, as the atmosphere warms due to rising levels of greenhouse gases, its concentration of water vapour increases, further intensifying the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is a natural, integral part of the Earth that keeps our world warm enough to sustain life. This process is known as the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect, where the natural process of warming caused by solar radiation and greenhouse gases is heightened by anthropogenic (i.e. Carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, water vapour effectively prevent some of this longwave radiation from leaving the atmosphere.
To learn more about Earth's changing climate, review the corresponding lesson on Greenhouse Gases and the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect. Similar examples can be drawn for warmer air temperatures increasing the rate of glacier and sea ice melting. This lesson covers the following objectives:.
Besides the enhanced greenhouse effect there are many other factors that aggravate climate change. A layer of gases in Earth's atmosphere naturally creates a greenhouse effect. Consequences of Global Warming.
For example, as the temperature of the earth’s surface increases more water vapour is evaporated. Clouds, ice caps and other light-colored surfaces reflect some light back into space, but most of the incoming energy reaches the planet’s surface. Humans beings are changing the face of the entire planet by destroying the rain forests and pumping our pollutants into the air and water.
Explain to the class the the greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring process that helps. 0 The problem comes with the carbon-altering activities that humans take part in, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other biomass, which puts more carbon into the atmosphere, causing the greenhouse effect. For example, the melting of the polar ice results in less of the sun’s energy being refl ected back to space;.
These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. Some gases in the atmosphere (the so called greenhouse gases:. The latter includes sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs).
Human activities and the greenhouse effect. For example, the melting of the Chacaltaya Glacier in Bolivia has exposed dark rocks beneath it. This is the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is contributing to warming of the Earth.
The problem we now face is that human activities – particularly burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), agriculture and land clearing – are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases. The amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere affects the strength of the. Without these gases in place, light and warmth from the sun would strike Earth, then largely.
Many scientists use the term “climate change” instead of “global warming.” This is because greenhouse gas emissions affect more than just temperature. Today however , major changes are taking place. Human activities are changing Earth's natural greenhouse effect.
Titan is a body with both a greenhouse effect and an anti-greenhouse effect. Many factories produce long-lasting industrial gases that do not occur naturally, yet contribute significantly to the enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming that is currently underway. This in turn causes more warming, which causes an additional increase in water vapour, in a self-reinforcing cycle.
Greenhouse Escape The Knight of Earth Create Playlist 2, a 10 minute playlist in Legends of Learning with 5 assessment questions from the Greenhouse Effect learning objective E n g a g e ( 1 0 m i n u t e s ) 1. However, an enhanced greenhouse effect due to human activity, such as burning fossil fuels for energy, can be detrimental to Earth's climate and ecology. Greenhouse effect refers to a process where thermal radiation from the earth’s surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and then radiated in all directions.
The presence of N 2, CH 4, and H 2 in the atmosphere contribute to a greenhouse effect, increasing the surface temperature by 21K over the expected temperature of the body with no atmosphere. The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth’s climate. The Earth radiates heat back toward space.
The Greenhouse Effect Definition Radiation:. Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Water Vapour, Nitrogen Trifluoride, Carbon Monoxide. This is leading to global warming.
The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect You now know that the greenhouse effect is both natural and necessary for our survival because it keeps Earth warm and hospitable. Greenhouse effect definition is - warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface. Trapping of extra infrared radiation as a result of the excessive amounts of greenhouse gases produced by humans.
Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F). The greatest example is that of. CF4 is a strong greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and has an atmospheric lifetime of 50,000 years.
Aerosols can control how much energy from the sun reaches the planet’s surface by changing the amount that is absorbed in the atmosphere and the amount that is scattered back out to space. The rocks absorb heat from the sun, speeding up the melting process. What must be remembered is that these changes will be superimposed on the pattern of warming due to the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Too many extra greenhouse gases turn the greenhouse effect into an enhanced greenhouse effect. Although the process is complex, the greenhouse effect can be described fairly simply:. Examples of Greenhouse Gases.
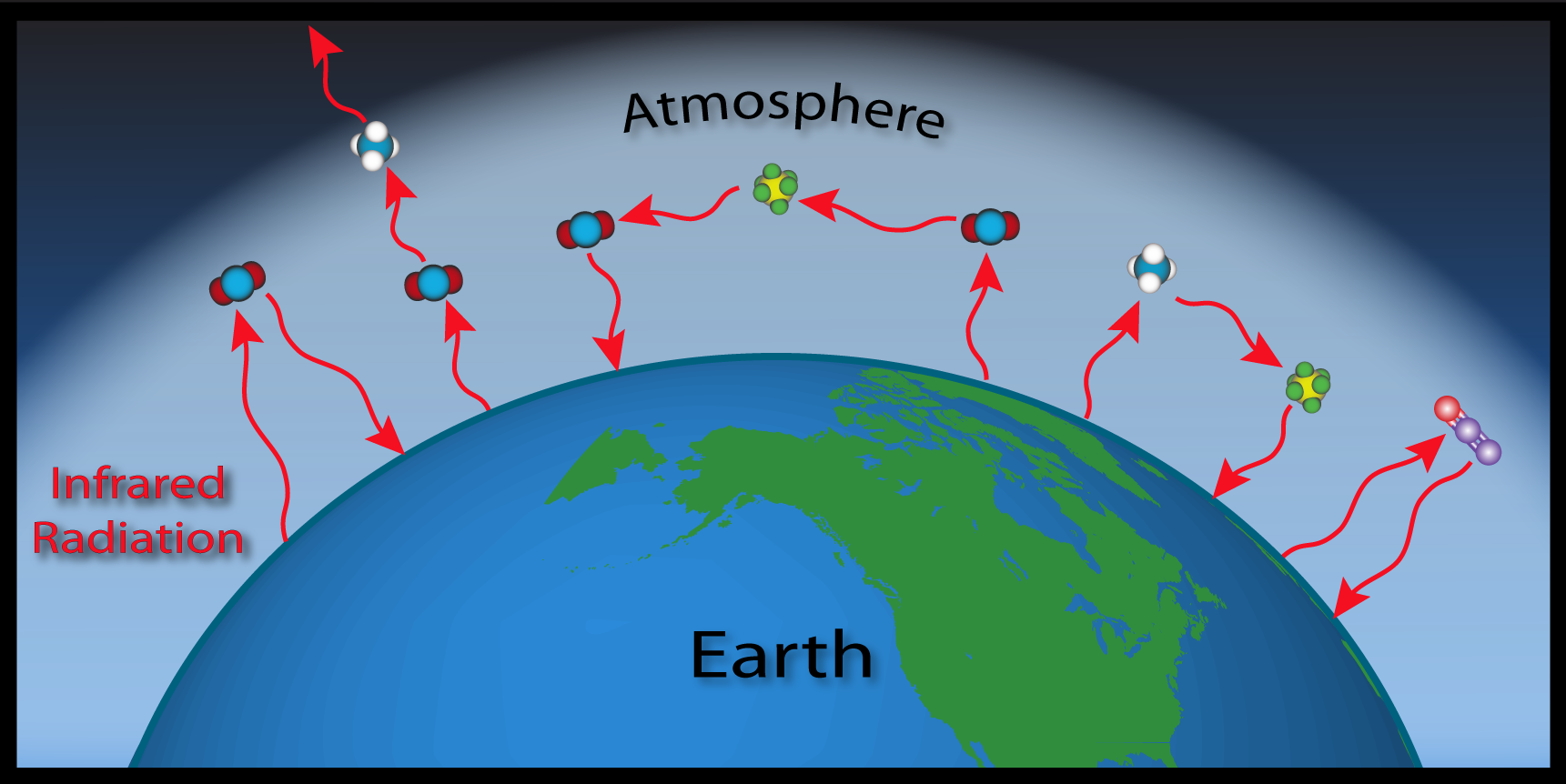
Naturally occurring heat-trapping gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, do not absorb the short-wave energy from the sun but do absorb the long-wave energy re-radiated from the Earth, keeping the planet much warmer than. Eventually these molecules then emit heat back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation. Energy that is propagated in the form of electromagnetic waves.
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. Deforestation also contributes to global warming. Incoming solar energy is called solar radiation Solar radiation warms the earth.
What is the enhanced Greenhouse Effect?. This is an example of positive feedback. As the ice melts it changes the surface characteristics of the surface as the underlying ocean or land will have a lower albedo than the ice and hence an enhanced ability to absorb solar radiation.
For example, CFC-12 is roughly 15,800 times more efficient molecule for molecule at trapping heat than CO 2. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist. The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect For the past ten thousand years the earth’s climate has been extremely good and beneficial to mankind.
It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun. Do all greenhouse gases have the same effect?. Image based on a figure from US EPA.
Additional trace gases produced by industrial activity that have greenhouse properties include nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and fluorinated gases (halocarbons). Https://www.spendmoretimeinthewild.co.uk Here at Spend More Time In The WILD we are not afraid to dr. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air.
Greenhouse Effect objective (in order):. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. The greenhouse effect is the increase in global temperatures which result from greenhouse gases trapping solar heat energy in the atmosphere.
Global Warming and the Greenhouse Effect Human induced climate change resulting from an enhanced greenhouse effect is probably the greatest environmental threat facing the world today. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60º F colder. Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun.
The burning of fossil fuels including coal, oil, and natural gas, along with the clearing of land for agricultural use and urban development, are increasing the amount of the heat-retaining greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. A stylized representation of the natural greenhouse effect. NASA has observed increases in the amount of carbon dioxide and some other greenhouse gases in our atmosphere.
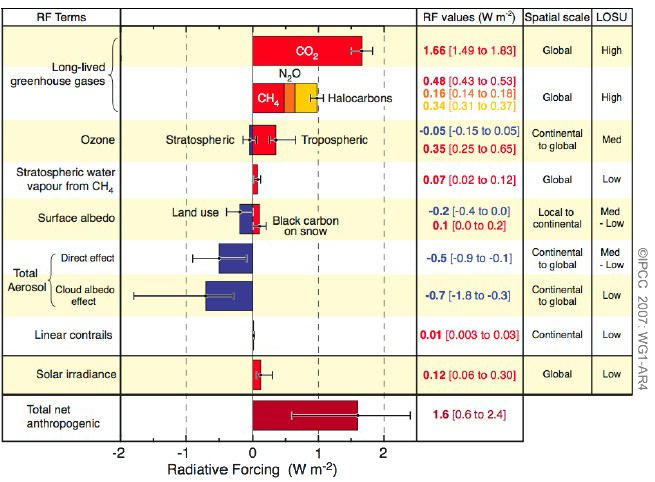
Because of its low concentration level in the atmosphere, it is not currently believed to have a significant radiative forcing effect, which leads to rising global temperatures. Burning fossil fuels like coal and oil puts more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere. Trees use carbon dioxide and give off oxygen in its place, which helps to create the optimal balance of.
It is believed by many experts to be the primary cause of global warming.Greenhouse gases include substances, such as CO2, nitrous oxide, methane and carbon monoxide. The Earth provides a unique life-supporting environment. The greenhouse effect is the natural way that the Earth keeps warm.
Each gas has different radiative properties, atmospheric chemistry, typical atmospheric lifetime, and atmospheric concentration. The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them. Specifically, the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide may be classified as the primary culprit.
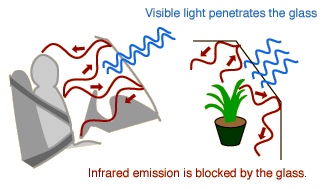
Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect refers to circumstances where the short wavelengths of visible light from the sun pass through a transparent medium and are absorbed, but the longer wavelengths of the infrared re-radiation from the heated objects are unable to pass through that medium. The greenhouse effect, combined with increasing levels of greenhouse gases and the resulting global warming, is expected to have profound implications, according to the near-universal consensus of. The existence of a high-altitude haze, which absorbs wavelengths of solar radiation but is transparent to infrared, contribute to an anti-greenhouse effect of approximately 9K.
Aerosols have a profound impact on the climate because, just like greenhouse gases, they are able to change the Earth’s “radiative”, or energy, balance. Some energy is re-emitted back into the atmosphere, as longwave radiation. A review of the topic including the physics of the greenhouse effect is given.
The Greenhouse Effect

Climate Change Human Factors Ppt Download

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

Causes Of Climate Change

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Untitled Document

Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay

The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect National Climate Assessment

Climate Change Ten Year Retreat

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Untitled Document

Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious
Q Tbn 3aand9gctvnzzq 9bxbbg50bcveuvdqog4rrg0mmi Unn1qdslab7xmg16 Usqp Cau

Global Warming Causes Effects And Solutions
Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids

Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Climate Change And Agriculture Wikipedia

Climate Change Feedback Wikipedia

Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
2

Greenhouse Gases And Temperature

Global Warming

Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrzrekt6ppooz5xslbdchmzqqxyfpr Mlogt C8 Wr7jkbzkspq Usqp Cau

Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming

Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqdqn3hrtggpwa2yxdsgbpthcktyf1idgi5cwnkwd Yzcnnkvbn Usqp Cau

Weatherquestions Com Everyday Examples Of The Greenhouse Effect
3

Paper On Greenhouse Effect Buy Original Essays Online Www Transetvih Net

Causes Of Climate Change

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

Solved Which Of The Following Is Not An Example Of Positi Chegg Com

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious

Is The Green House Effect Operating In Earth S Atmosphere Helpful Or Essay

Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Venus And The Greenhouse Effect

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici

Geog 101 Exam 1 Essay 2 Grade A Physical Geography Studocu

5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica

Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society

Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Nys Dept Of Environmental Conservation

Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
Climate Change Online Presentation

Solved Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Negative Chegg Com

Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
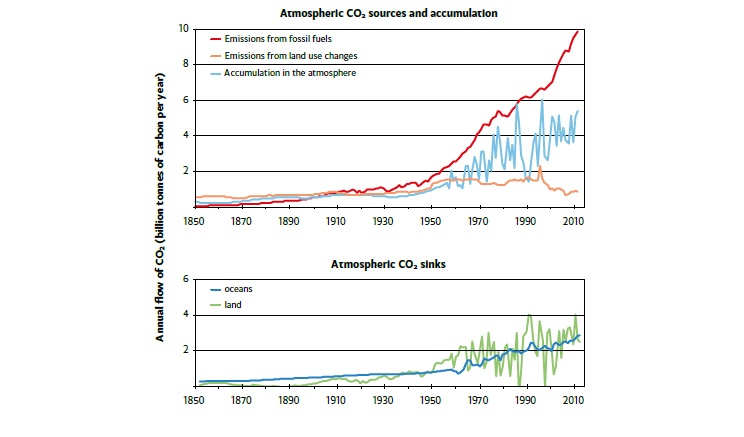
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Vce Environmental Science Ppt Download
3 Are Human Activities Causing Climate Change Australian Academy Of Science

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
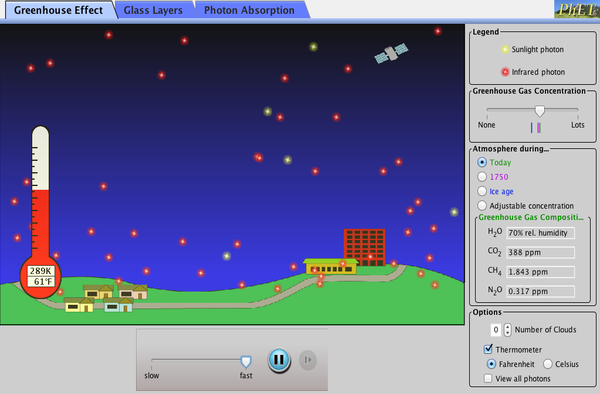
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Heat Phet Interactive Simulations
2

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
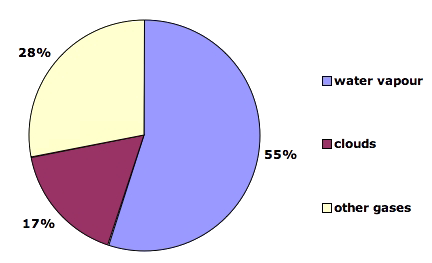
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
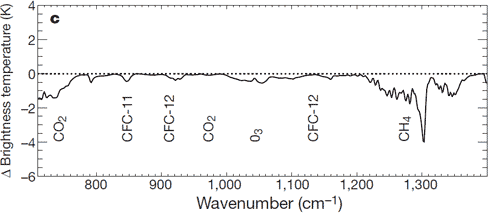
How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
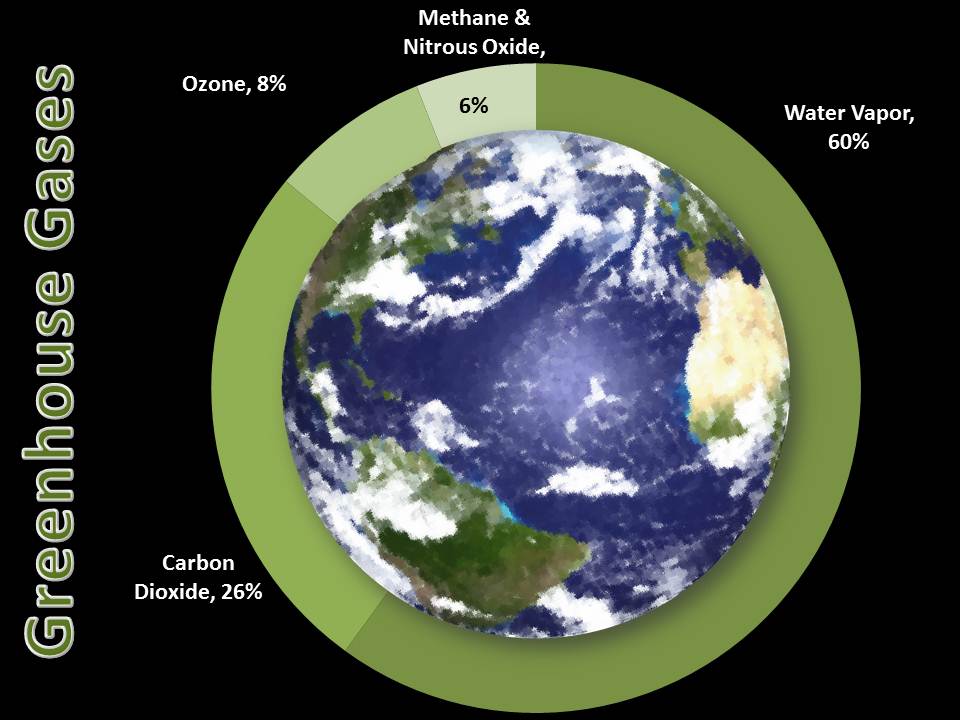
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

Solved Question 3 1 Pts Which Of The Following Is An Exam Chegg Com
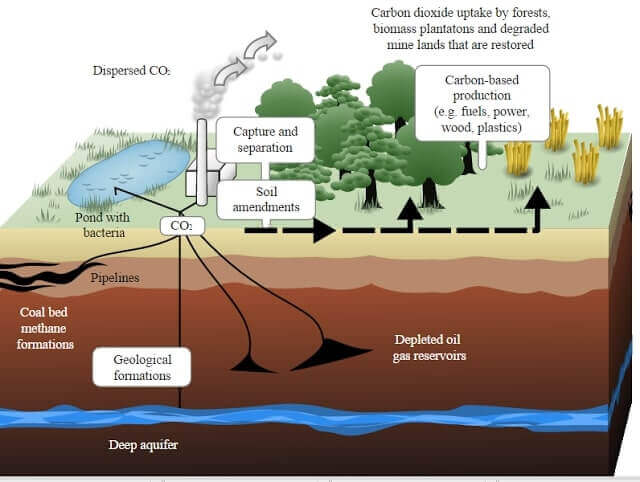
Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias
The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Climate Change Human Factors Ppt Download
Creative Writing Assignment 1 Ib Biology
Atmo336 Fall
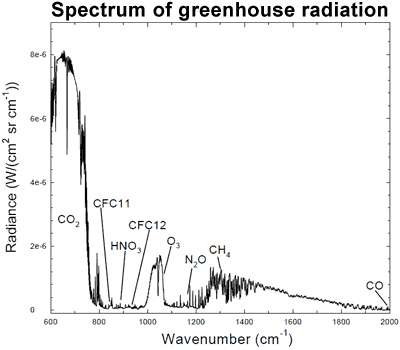
How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming

Pdf Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Global Warming 18 1 Introduction
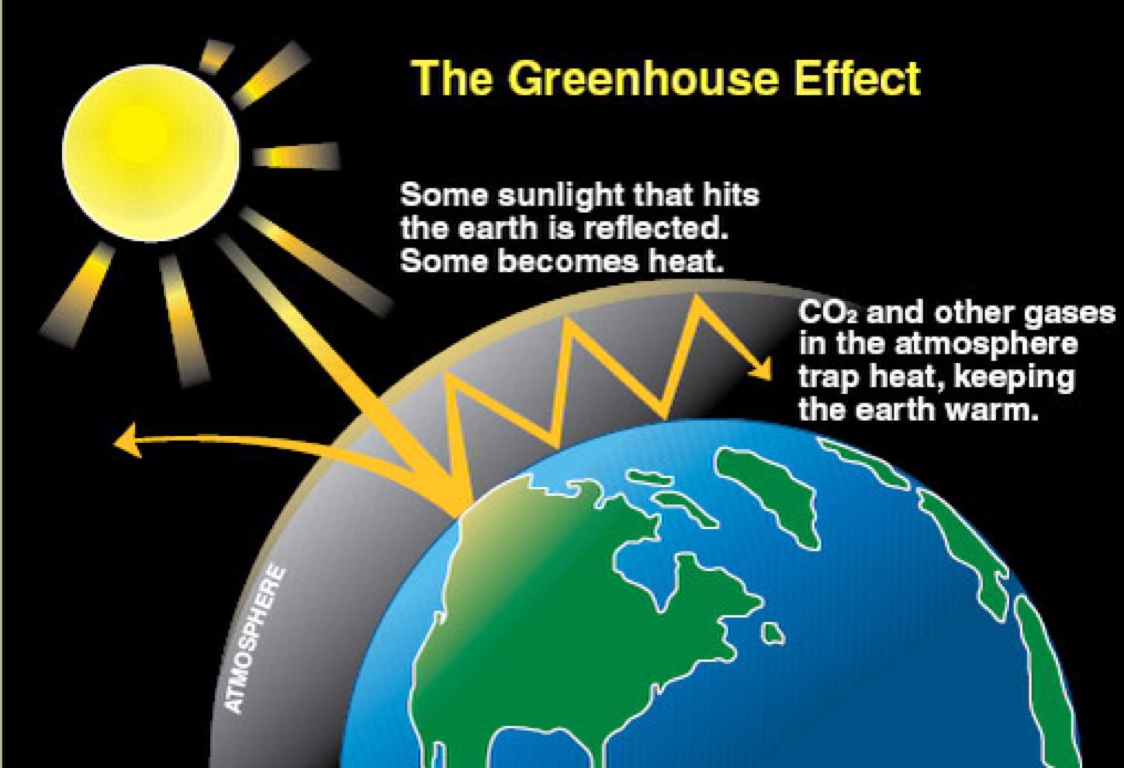
What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
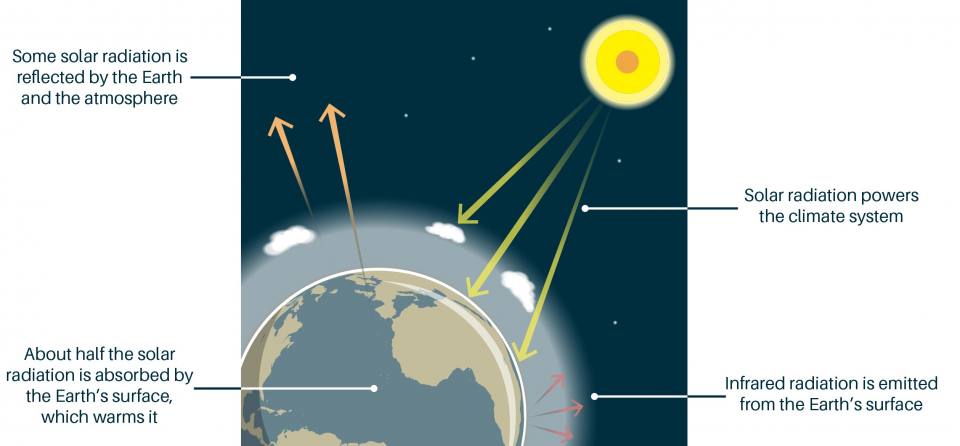
The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey

Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems

Climate Change Feedback Wikipedia

Identifying Feedback Practice

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious

Causes Of Climate Change Nsw Department Of Primary Industries

Solved Science 30 Climate Change To The Human Influence Chegg Com
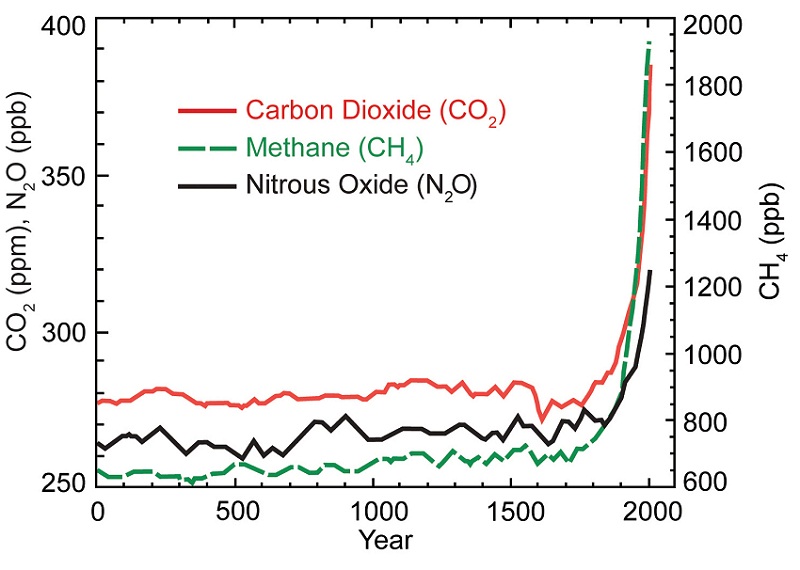
Causes Of Climate Change Climate Change Science Us Epa

Global Warming What Are The Major Effects Problems Of Global Warming And How Can They Be Solved By Senthuran Sivasambo Rohit Jogendran Walid Masud Ppt Download

The Greenhouse Effect Youtube

25 Wonderful Ways To Reduce Greenhouse Gases Conserve Energy Future

Enhanced Greenhouse Gas Effect In 45 Seconds Youtube



